Main components of a turbocharger
Components of a turbocharger
The main components of the turbocharger are the housing (including the turbine housing and the compressor housing), the wheels (including the turbine wheel and the compressor wheel). The exhaust gas drives the turbine to generate power, and the turbine drives the compressor wheel to compress air), and the intermediate body (internal There are lubricating oil channels and bearings, responsible for heat dissipation and friction reduction), sealing rings (responsible for sealing), pressure relief valves (at the moment of oil collection, because the engine does not need to generate so much power, there is no need for a large amount of air to enter At this time, the pressure is still generated by the turbocharger due to the inertial rotation of the cylinder. At this time, a pressure relief valve is required to release the pressure to prevent damage to the components due to excessive pressure)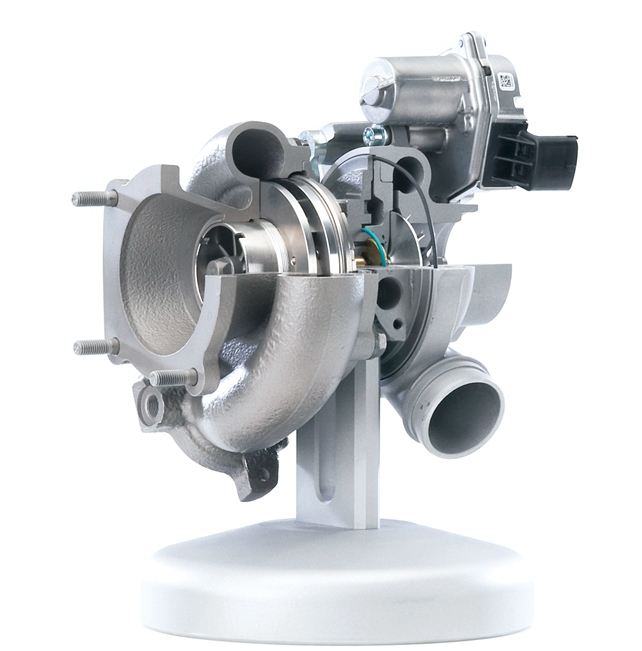
In real work, because the compressor wheel compressed air will increase the air temperature, too high intake air temperature will reduce the efficiency of the engine, so an intercooler that cools the air is needed to assist.

Similar to the Supercharger (Supercharger, Super-Charger) function, both can increase the air flow into the internal combustion engine or the boiler, thereby improving the efficiency of the machine. Commonly used in automobile engines, turbochargers can increase the horsepower output of internal combustion engines by using the heat and flow of exhaust gas.





